Microsoft has announced the general availability of Azure Availability Zones to provide a high availability option for their customer’s mission-critical applications and data. Availability Zones provide isolated locations within a geographic region, allowing services and data to replicated to increase fault tolerance. Last year during Ignite, an annual conference for developers and IT professionals, Microsoft first introduced Azure Availability Zones.
With Azure Availability zones, customers can deploy fault-tolerant applications with high availability in regions with availability zones. Mitch Nelson, Director, Managed Services, Adobe, said in the blog post about the announcement of the general availability of availability zones:
Availability Zones give us the combination of low latency and high availability that we need to meet customer requirements. All of my teams’ applications with higher SLA levels are now built on Availability Zones. The physical separation of Availability Zones builds an extra layer of redundancy.
Today two Azure regions, Europe (France Central) and the United States (US Central), offer availability zones, and three more regions have them in preview: East US 2, West Europe, and Southeast Asia. These availability zones are physically separate locations within an Azure region. Moreover, each availability zone consists of one or more data centers equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. Also, to ensure resiliency, there will be a minimum of three separate zones in all enabled regions.

Image source: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/global-infrastructure/regions/
With the physical separation of availability zones in a region, data and applications will be less affected by hardware failures in a data center. So-called zone-redundant services will replicate data and applications between zones to prevent single-point-of-failures. Furthermore, customers can pin resources like virtual machines, managed disks, and IP-addresses to a specific zone.
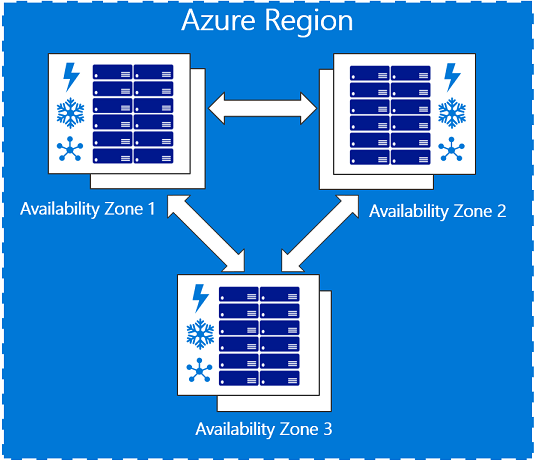
Image source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/availability-zones/az-overview
The three big cloud providers Microsoft, Amazon, and Google host cloud services in multiple locations around the world. Moreover, each provider now has the concept of regions, a separate geographic area, and isolated locations known as (availability) zones. Both Amazon and Google have had availability zones for some time now and are more spread across the globe, however, not every region supporting availability zones has a minimum of three separate zones, in contrast to the Microsoft regions with availability zones. Some have two, others have more.
With Availability Zones, Microsoft will offer an SLA of 99.99% for uptime of Virtual Machines (VMs) when running in two or more availability zones. Deploying Virtual Machines in an availability zone comes at no extra cost. However, there will be charges for inter-Availability Zone VM-to-VM data transfers. For more details on pricing see the bandwidth pricing page. Furthermore, Microsoft is planning to bring availability zones in other regions of the world.