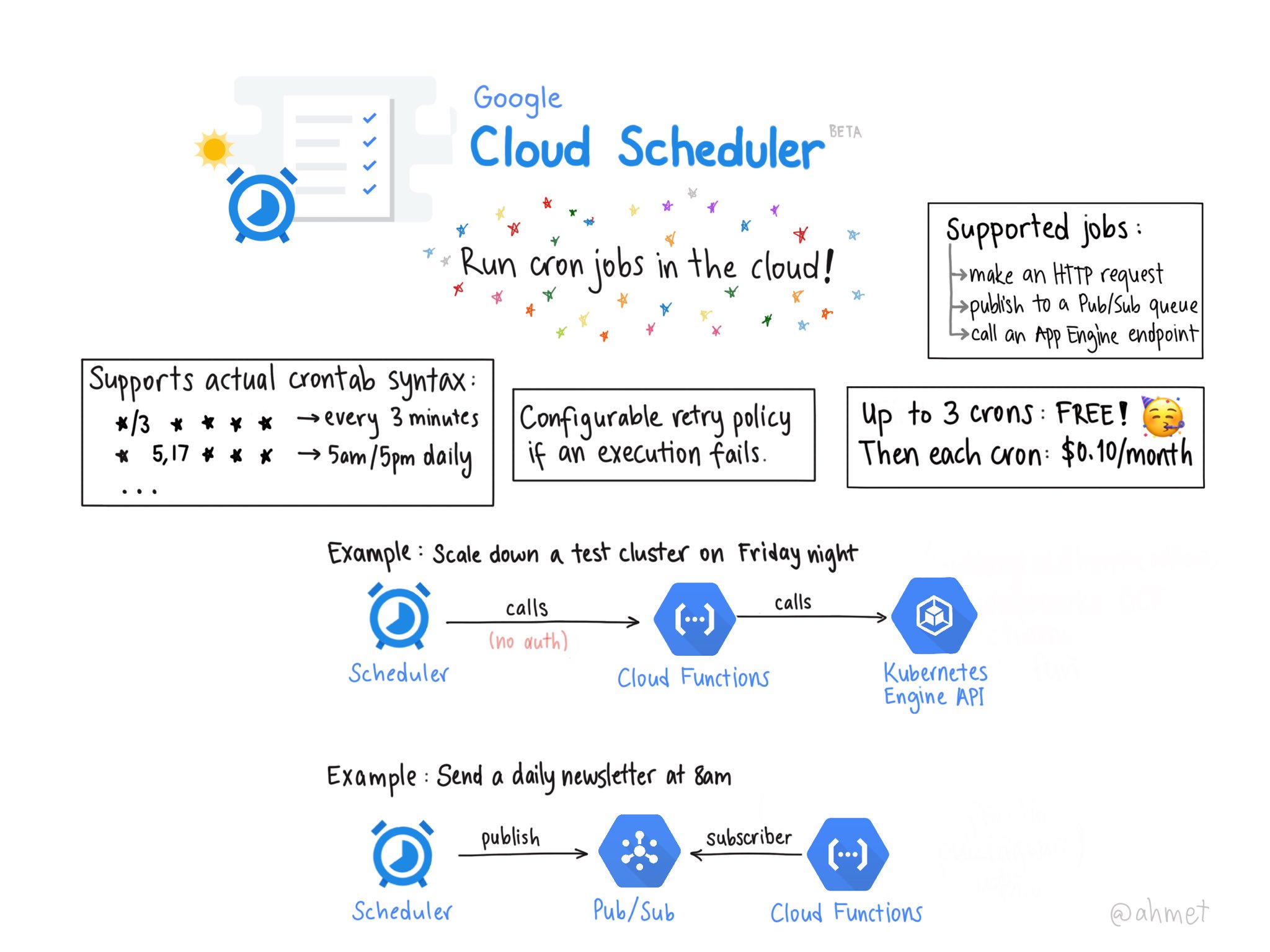
In a recent blog, Google announced that customers can now securely invoke HTTP targets on a schedule using Cloud Scheduler – a fully managed cron job service that allows any application to invoke batch, big data, and cloud infrastructure operations.
Google made Cloud Scheduler generally available (GA) during its Next event two months ago in San Francisco, and after several months of its beta launch, as reported on earlier by InfoQ. Since the GA release, Google has added a new feature that allows customers to trigger any service, running anywhere: on-prem, on Google Cloud or any third-party datacenter. Moreover, users can now, according to the blog post, securely invoke HTTP targets on a schedule to reach services running on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Compute Engine, Cloud Run, Cloud Functions, or on on-prem systems or elsewhere with a public IP using industry-standard OAuth or OpenID Connect authentication.
With Cloud Schedulers, users can perform various tasks such as trigger CI/CD pipelines, schedule database updates and push notifications, and invoke cloud functions.
Source: https://pbs.twimg.com/media/Dr_pavEVYAIWq4v.jpg:large
Furthermore, users benefit from the tight integration with most of Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services and cost-saving. Romin Irani, partner engineer, Google Cloud, gave a cost-saving example in a tweet:
Left your dev VMs in the cloud running and ran up a bill? We've all done that. How about an automated schedule that stops all VMs labelled "dev" at 5 pm and restarts them at 9 am?
Users can schedule a job in Cloud Scheduler by using its UI, or the CLI or API to invoke an HTTP/S endpoint, Cloud Pub/Sub topic or App Engine application. When a job starts, it will send Cloud Pub/Sub message or an HTTP request to a specified target destination on a recurring schedule. Subsequently, the target handler will execute the job and return a response of the outcome – either:
- A success code (2xx for HTTP/App Engine and 0 for Pub/Sub) when it succeeds
- Or an error, resulting in the Cloud Scheduler retrying the job until it reaches the maximum number of attempts
Furthermore, once user schedules a job, they can monitor this in the Cloud Scheduler UI and check the status.
Google Cloud Scheduler is not the only managed cron service available in the public cloud. Competitors Microsoft and Amazon already offered a scheduler service that has been available for quite some time. Microsoft offers the Azure Scheduler service, which became generally available in late 2015 and will be replaced by Azure Logic Apps Service, where developers can use the scheduler connector. Also, Logic Apps offers additional capabilities for application and process integration, data integration and B2B communication. Furthermore, AWS released the Batch service with similar capabilities to Scheduler in late 2016. Here developers can schedule functions with cron in AWS Lambda, similar to how Google Scheduler invokes Cloud Functions.
Pricing details, including calculator, are available on the Google Scheduler pricing page.
